Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (52): 8414-8419.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.52.010
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of different drug eluting stents on inflammatory factors in elderly patients with non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome
Lu Miao, Wang Xiang-ming, Wang Sen, Zhou Chuan-wei
- Department of Geriatric Cardiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210029, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Revised:2014-11-18Online:2014-12-17Published:2014-12-17 -
Contact:Zhou Chuan-wei, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Geriatric Cardiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210029, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Lu Miao, Master, Attending physician, Department of Geriatric Cardiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210029, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China for the Youth, No. 81100123
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Lu Miao, Wang Xiang-ming, Wang Sen, Zhou Chuan-wei. Effects of different drug eluting stents on inflammatory factors in elderly patients with non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(52): 8414-8419.
share this article
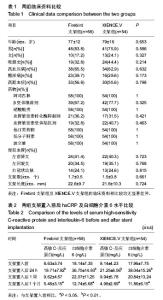
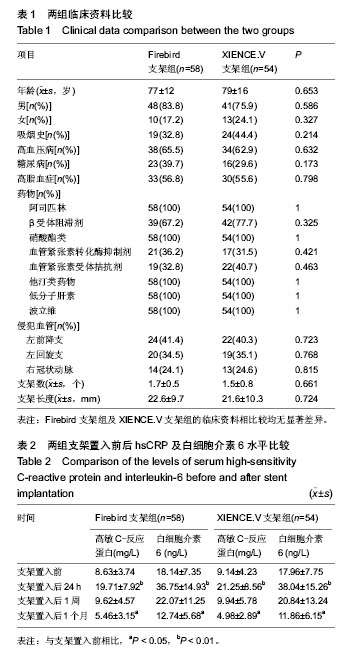
2.1 受试者数量分析 纳入Firebird支架组患者58例,XIENCE.V支架组患者54例,全部进入结果分析,无脱落。 2.2 受试者基线分析 Firebird支架组及XIENCE.V支架组的临床资料相比较,无论是年龄、性别、合并疾病、服药情况等临床指标,还是冠脉造影结果及置入支架数均差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见表1。 2.3 炎症指标检测结果 见表2。两组经皮冠状动脉介入治疗临床指标、冠脉病变情况以及经皮冠状动脉介入治疗手术基本参数比较均差异无显著性意义。置入前Firebird支架组与XIENCE.V支架组比较,高敏C-反应蛋白及白细胞介素6均差异无显著性意义。两组置入后24 h与置入前相比高敏C-反应蛋白及白细胞介素6均有显著升高(P < 0.01);两组置入后1周高敏C-反应蛋白及白细胞介素6略下降,但与置入前无显著差异;两组置入后1个月高敏C-反应蛋白及白细胞介素6均有显著下降(P < 0.05)。置入后24 h、 1周、1个月,Firebird支架组与 XINCE.V支架组相比高敏C-反应蛋白及白细胞介素6差异无显著性意义。 2.4 置入后不良反应及生物相容性分析 按不同类型支架分为两组,分组后所有病例均完成1个月的随访及检测,并按医嘱进行了规范双联抗血小板治疗;期间合并其他用药情况相似,均无心脏事件及死亡发生,生物相容性均较好。"
| [1] 姚丽梅.国产雷帕霉素支架置入后血管再狭窄与炎症指标的变化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(43): 8446-8449. [2] 克非,尹栋,昊元,等.成功置入FIREBIRD支架和CYPHER支窦架远期临床疗效比较:单中心注册研究分析结果[J].中国循环杂志, 2012,27(2):99-102. [3] 聂绍平.依维莫司洗脱支架用于冠心病安全性和有效性的新证据[J].心血管病学进展,2012,33(6):683-685. [4] Riezebos RK, Verheugt FW, Laarman GJ, et al.The biochemical aspects of a non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2012;13(2-3):e70-e76. [5] Jukema JW, Verschuren JJ, Ahmed TA,et al. Restenosis after PCI. Part 1: pathophysiology and risk factors. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2011;9(1):53-62. [6] 李晓涛.炎症反应在冠脉支架置入后再狭窄中的研究进展[J].心血管病学进展,2007,28(5):703-705. [7] 逢淑峰,徐大海,赵利华.冠状动脉内支架置入后再狭窄与炎症反应[J].实用心脑肺血管病杂志,2011,19(20):163-165. [8] 裴汉军.药物洗脱支架再狭窄治疗的研究进展[J].心血管病学进展, 2013,34(2):174-177. [9] Sun D, Zheng Y, Yin T, et al. Coronary drug-eluting stents: from design optimization to newer strategies. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2014;102(5):1625-1640. [10] 赵慧强,郭文怡,贾国良,等.雷帕霉素洗脱支架对冠心病患者介入置入后血炎症因子的影响[J].中国循环杂志,2005,20(2):98-101. [11] 庞明杰,张宏,赵燕,等.依维莫司洗脱支架在急性冠脉综合征中应用的效果分析[J].医学前沿,2013,4:20-21. [12] Anderson JL, Adams CD, Antman EM, et al. 2012 ACCF/AHA focused update incorporated into the ACCF/AHA 2007 guidelines for the management of patients with unstable angina/non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction: a report of the american college of cardiology foundation/american heart association task force on practice guidelines. Circulation. 2012,126(7):875-910. [13] 刘治军.2012年ACCF/AHA对不稳定心绞痛/非ST段抬高的心肌梗死患者管理的指南更新简介[J].药品评价,2013,10(22):19-24. [14] 许春平,赵献明,曾波,等.阿托伐他汀预处理对非杂栽抬高急性冠脉综合征患者行冠脉支架置入后炎性因子和预后的影响[J].河北医药,2013,19(8):1202-1204. [15] 杨帆,赵雅琳,葛华.冠心病患者行冠状动脉支架置入后外周血小板P-选择素及血清hsCRP的动态变化[J].中国试验诊断学,2010, 14(7):1117-1118. [16] 吴铮,李文铮,李世英.介入治疗对老年冠心病患者脑钠肽和超敏C反应蛋白水平的影响[J].中国基层医药,2014,21(8):1132-1133. [17] 章敏,蒋红丽.老年冠心病支架置入后血清IL-6与TNF-α水平改变及黄芪注射液的干预作用[J].中国实用诊断与治疗杂志, 2008, 22(11):832-834. [18] 莫文,焦桂萍,袁志柳,等.血清hsCRP, TNF-α, IL-6, 血脂水平对慢性脑供血不足的诊断价值[J].中国试验方剂学杂志, 2011, 17(13): 235-236. [19] Ramasamy I. Biochemical markers in acute coronary syndrome. Clin Chim Acta. 2011;412(15-16):1279-1296. [20] Sami S, Willerson JT. Contemporary treatment of unstable angina and non-ST-segment-elevation myocardial infarction (part 2). Tex Heart Inst J. 2010;37(3):262-275. [21] Koenig W. High-sensitivity C-reactive protein and atherosclerotic disease: from improved risk prediction to risk-guided therapy. Int J Cardiol. 2013;168(6):5126-5134. [22] 毛庆录,宋书凯,李敬田.急性冠脉综合征支架置入后早期血清hsCRP、MMP-9、IL-18的变化及意义[J].山东医药,2009,49(9): 6-8. [23] Hartman J, Frishman WH. Inflammation and atherosclerosis: a review of the role of interleukin-6 in the development of atherosclerosis and the potential for targeted drug therapy. Cardiol Rev. 2014;22(3):147-151. [24] 王远东,刘敏.冠状动脉支架置入后C-反应蛋白、白介素-6的变化及意义[J].健康必读杂志,2012,8(8):281. [25] 佟子川,张建军,魏好,等.不同类型药物洗脱支架介入治疗对血清C反应蛋白和白细胞介素6水平的影响[J].临床心血管病杂志, 2010,26(10):766-769. [26] 王子超,刘静,高传玉,等.冠状动脉雷帕霉素洗脱支架置入对患者血清CRP及IL-2水平的影响及临床价值[J].心脑血管病防治, 2008,8(1):31-32. [27] 卢强.冠状动脉支架置入置入后早期炎性标记物的观察[J].河北医药,2009,31(20):2738-2739. [28] 刘晨,王智慧.IL-6、IL-8水平与冠状动脉支架置入置入后再狭窄相关性分析[J].中国试验诊断学,2011,15(1):99-101. [29] Giordano A, Romano A. Inhibition of human in-stent restenosis: a molecular view. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2011; 11(4):372-377. [30] 杜健鹏.冠状动脉药物涂层支架后再狭窄与炎症反应的相关性[J].心血管病学进展,2009,30(5):791-794. [31] Chaabane C, Otsuka F, Virmani R, et al. Biological responses in stented arteries. Cardiovasc Res. 2013;99(2):353-363. [32] Okura H, Takagi T, Yoshida K. Therapies targeting inflammation after stent implantation. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2013;11(4):399-406. [33] Palmerini T, Biondi-Zoccai G, Della Riva D, et al. Stent thrombosis with drug-eluting stents: is the paradigm shifting? J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62(21):1915-1921. [34] 张书富,郑鹏翔,陈德,等.国产Firebird支架在急性冠状动脉综合征急诊介入治疗中的作用[J].实用医学杂志,2009,25(4): 593-595. [35] 郑雨田.新一代冠状动脉药物洗脱支架临床应用进展[J].国际生物医学工程杂志,2012,35(5):312-316. [36] Onuma Y, Serruys PW, Muramatsu T, et al. Incidence and imaging outcomes of acute scaffold disruption and late structural discontinuity after implantation of the absorb everolimus-eluting fully bioresorbable vascular scaffold: optical coherence tomography assessment in the absorb cohort b trial (a clinical evaluation of the bioabsorbable everolimus eluting coronary stent system in the treatment of patients with de novo native coronary artery lesions). JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2014;7(12):1400-1411. [37] Wöhrle J, Naber C, Schmitz T, Schwencke C, et al. Beyond the early stages: insights from the ASSURE registry on bioresorbable vascular scaffolds. EuroIntervention. 2014 doi: 10.4244/EIJY14M12_10. [38] Takashima A, Shimabukuro M, Tabata M, et al. Histopathological heterogeneity of in-stent restenosis in four coronary endarterectomy specimens. Cardiovasc Pathol. 2014. doi: 10.1016/j.carpath.2014.11.002. [39] Luca T, Giuseppe BZ, Fabrizio T, et al. Italian Diffuse/Multivessel Disease ABSORB Prospective Registry under the auspices of Società Italiana di Cardiologia Invasive-GISE (IT-DISAPPEARS): study design and rationale. J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown). 2014 [Epub ahead of print]. [40] Wiebe J, Liebetrau C, Dörr O, et al. Feasibility of everolimus-eluting bioresorbable vascular scaffolds in patients with chronic total occlusion. Int J Cardiol. 2015;179: 90-94. [41] Cho S, Shin D, Kim J, et al. Rationale and design: Impact of intravascular ultrasound guidance on long-term clinical outcomes of everolimus-eluting stents in long coronary lesions. Contemp Clin Trials. 2014;40C:90-94. [42] Kochman J, Tomaniak M, Pietrasik A, et al. Bioresorbable everolimus-eluting vascular scaffold in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: Optical coherence tomography evaluation and clinical outcomes. Cardiol J. 2014. doi: 10.5603/CJ.a2014.0090. [43] Won H, Kang TS, Hong BK, et al. Neointimal response to second-generation drug-eluting stents in diabetic patients with de-novo coronary lesions: intravascular ultrasound study. Coron Artery Dis. 2014 [Epub ahead of print]. [44] Karbassi A, Kassaian SE, Poorhosseini H, et al. Selective versus exclusive use of drug-eluting stents in treating multivessel coronary artery disease: a real-world cohort study. Tex Heart Inst J. 2014;41(5):477-483. [45] Adriaenssens T, Ughi GJ, Dubois C, et al. STACCATO (Assessment of Stent sTrut Apposition and Coverage in Coronary ArTeries with Optical coherence tomography in patients with STEMI, NSTEMI and stable/unstable angina undergoing everolimus vs. biolimus A9-eluting stent implantation): a randomised controlled trial. EuroIntervention. 2014. doi: 10.4244/EIJY14M11_11. [46] Doostzadeh J, Clark LN, Bezenek S, et al. Recent progress in percutaneous coronary intervention: evolution of the drug-eluting stents, focus on the XIENCE V drug-eluting stent. Coron Artery Dis. 2010;21(1):46-56. [47] 刘小熊,夏豪,万埝,等.依维莫司药物洗脱支架与西罗莫司药物洗脱支架治疗冠心病疗效的Meta分析[J].中国循证心血管医学杂志,2013,5(2):111-115. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||